The empirical formula and molecular formula worksheet delves into the fascinating world of chemical formulas, providing a comprehensive exploration of their concepts, determination, and relationship. This engaging resource empowers learners to unravel the intricacies of molecular structures, fostering a deeper understanding of chemical composition.
Throughout this worksheet, we embark on a journey to unravel the mysteries of empirical formulas, their significance in representing the simplest whole-number ratio of elements in a compound, and the techniques for deducing them from experimental data. We then delve into the realm of molecular formulas, exploring their role in depicting the exact number and arrangement of atoms within a molecule, and the methods for determining them based on empirical formulas and molar masses.
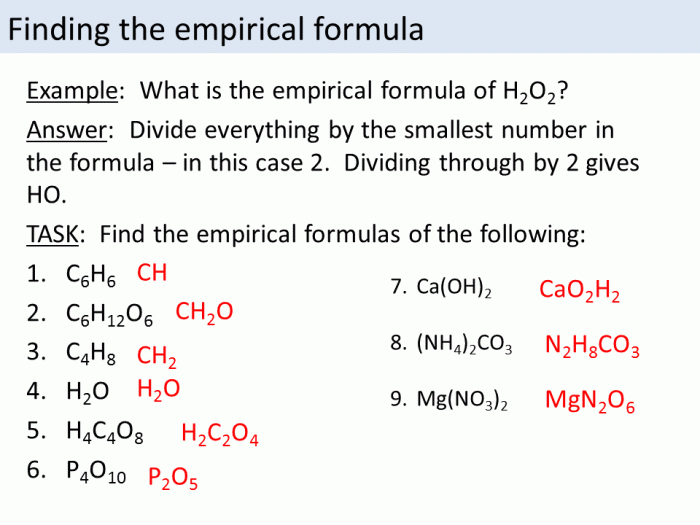
Empirical Formula
An empirical formula is a chemical formula that represents the simplest whole-number ratio of the atoms present in a compound. It does not provide any information about the molecular structure or the arrangement of atoms within the molecule.
Examples of empirical formulas:
- CH 2O (formaldehyde)
- C 6H 12O 6(glucose)
- NaCl (sodium chloride)
Determining the empirical formula from experimental data:
- Determine the mass of each element present in the compound.
- Convert the mass of each element to moles.
- Divide the number of moles of each element by the smallest number of moles.
- Simplify the resulting mole ratios to whole numbers.
Molecular Formula

A molecular formula is a chemical formula that represents the actual number and arrangement of atoms in a molecule. It provides complete information about the composition and structure of the molecule.
Examples of molecular formulas:
- CH 4O (methanol)
- C 6H 12O 6(glucose)
- NaCl (sodium chloride)
Determining the molecular formula from experimental data:
- Determine the empirical formula of the compound.
- Determine the molar mass of the compound.
- Divide the molar mass by the empirical formula mass.
- Multiply the empirical formula by the resulting factor to obtain the molecular formula.
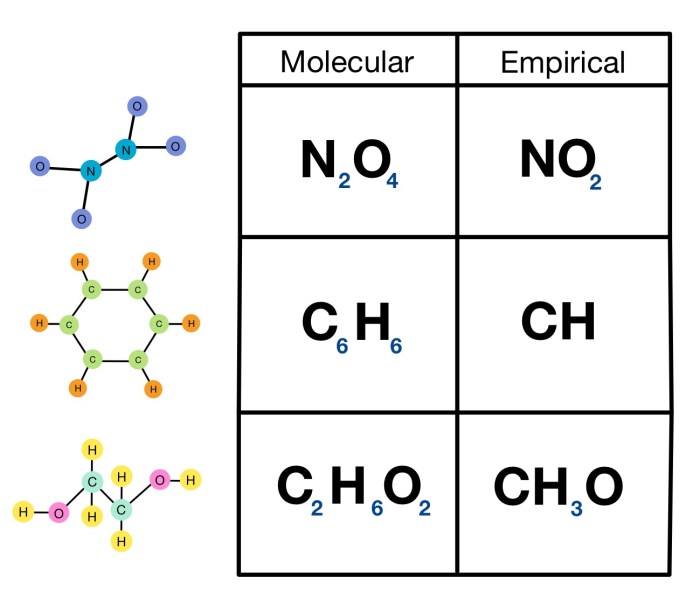
Relationship between Empirical Formula and Molecular Formula

The empirical formula and molecular formula of a compound are related by a simple factor, which is known as the molecular formula multiplier. This factor represents the number of empirical formula units present in the molecular formula.
Examples:
- The empirical formula of glucose is CH 2O, and its molecular formula is C 6H 12O 6. The molecular formula multiplier is 6, indicating that the molecular formula is six times the empirical formula.
- The empirical formula of sodium chloride is NaCl, which is also its molecular formula. This indicates that the molecular formula multiplier is 1.
Converting between empirical formula and molecular formula:
- Determine the empirical formula of the compound.
- Determine the molecular formula multiplier.
- Multiply the empirical formula by the molecular formula multiplier to obtain the molecular formula.
Query Resolution: Empirical Formula And Molecular Formula Worksheet
What is the difference between an empirical formula and a molecular formula?
An empirical formula represents the simplest whole-number ratio of elements in a compound, while a molecular formula depicts the exact number and arrangement of atoms within a molecule.
How can I determine the empirical formula from experimental data?
To determine the empirical formula, you need to find the mass percentages of each element in the compound and convert them to mole ratios, then simplify the ratios to the smallest whole numbers.
How can I convert between an empirical formula and a molecular formula?
To convert between an empirical formula and a molecular formula, you need to know the molar mass of the compound. The molecular formula will be a multiple of the empirical formula, with the multiple being equal to the ratio of the molar mass to the empirical formula mass.